Product Description
mini quiet home use food package sealer oilless vacuum air pump
Advantages:
Oil-less Vacuum Pumps / Air Compressors
PRANSCH oil-less rocking piston pump and air compressor combines the best characteristics of traditional piston pumps(air compressor) and diaphragm pumps into small units with excellent features.
- Light weight and very portable
- Durable and near ZERO maintenance
- Thermal protection (130 deg C)
- Power cord with plug, 1m length
- Shock mount
- Silencer – muffler
- Stainless steel vacuum and pressure gauge, both with oil damping
- Two stainless steel needle valves each with lock nut.
- All nickel plated fittings
- Power supply 230V, 50/60 Hz
This series is ideal for use in applications where oil-mist is undesirable. For examples, pressure/vacuum filtration, air sampling, water aeration, flame photometer, etc.
Specification:
| Model | Frequency | Flow | Pressure | Power | Speed | Current | Voltage | Heat | Sound | Weight | Hole | Installation Dimensions |
| Hz | L/min | Kpa | Kw | Min-1 | A | V | 0 C | db(A) | Kg | MM | MM | |
| PM200V | 50 | 33 | -84 | 0.10 | 1380 | 0.45 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | 5 | L100xW74 |
| 60 | 50 | -84 | 0.12 | 1450 | 0.90 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 48 | 1.8 | 5 | ||
| PM300V | 50 | 66 | -86 | 0.12 | 1380 | 0.56 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 50 | 3.2 | 6 | L118xW70 |
| 60 | 75 | -86 | 0.14 | 1450 | 1.13 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 50 | 3.2 | 6 | ||
| PM400V | 50 | 80 | -92 | 0.32 | 1380 | 0.95 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | L153xW95 |
| 60 | 92 | -92 | 0.36 | 1450 | 1.91 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | ||
| PM550V | 50 | 100 | -92 | 0.32 | 1380 | 1.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | L148xW83 |
| 60 | 110 | -92 | 0.36 | 1450 | 3.10 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 56 | 6.0 | 6 | ||
| PM1400V | 50 | 166 | -92 | 0.45 | 1380 | 1.90 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | 6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 183 | -92 | 0.52 | 1450 | 4.10 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 58 | 8.5 | 6 | ||
| PM2000V | 50 | 216 | -92 | 0.55 | 1380 | 2.50 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 60 | 9.0 | 6 | L203xW86 |
| 60 | 250 | -92 | 0.63 | 1450 | 5.20 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 60 | 9.0 | 6 | ||
| HP2400V | 50 | 225 | -94 | 0.90 | 1380 | 3.30 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | 7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 258 | -94 | 1.10 | 1450 | 6.90 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 75 | 17.0 | 7 | ||
| PM3000V | 50 | 230 | -94 | 1.10 | 1380 | 4.20 | 210/235 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | 7 | L246xW127 |
| 60 | 266 | -94 | 1.30 | 1450 | 8.50 | 110/125 | 5-40 | 76 | 17.5 | 7 |
Why use a Rocking Piston Product?
Variety
Pransch oilless Rocking Piston air compressors and vacuum pumps, available in single, twin, miniature, and tankmounted
styles, are the perfect choice for hundreds of applications. Choose from dual frequency, shaded pole,
and permanent split capacitor (psc) electric motors with AC multi-voltage motors to match North American,
European, and CHINAMFG power supplies. A complete line of recommended accessories as well as 6, 12, and
24 volt DC models in brush and brushless types are also available.
Performance
The rocking piston combines the best characteristics of piston and diaphragm air compressors into a small unit
with exceptional performance. Air flow capabilities from 3.4 LPM to 5.5 CFM (9.35 m3/h), pressure to 175 psi
(12.0 bar) and vacuum capabilities up to 29 inHg (31 mbar). Horsepowers range from 1/20 to 1/2 HP
(0.04 to 0.37 kW).
Reliable
These pumps are made to stand up through years of use. The piston rod and bearing assembly are bonded
together, not clamped; they will not slip, loosen, or misalign to cause trouble.
Clean Air
Because CHINAMFG pumps are oil-free, they are ideal for use in applications in laboratories, hospitals, and the
food industry where oil mist contamination is undesirable.
Application:
- Transportation application include:Auto detailing Equipment,Braking Systems,Suspension Systems,Tire Inflators
- Food and Beverage application include:beverage dispensing,coffee and Espresso equipment,Food processing and packaging,Nitrogen Generation
- Medical and laboratory application include:Body fluid Analysis equipment,Dental compressors and hand tools,dental vacuum ovens,Dermatology equipment,eye surgery equipment,lab automation,Liposuction equipment,Medical aspiration,Nitrogen Generation,Oxygen concentrators,Vacuum Centrifuge,vacuum filtering,ventilators
- General industrial application include:Cable pressurization,core drilling
- Environmental application include:Dry sprinkler systems,Pond Aeration,Refrigerant Reclamation,Water Purification Systems
- Printing and packaging application include:vacuum frames
- material Handling application include:vacuum mixing
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Reciprocating Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Positive Displacement Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Mainsuction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Dry |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
How Do Vacuum Pumps Contribute to Energy Savings?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in energy savings in various industries and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through several mechanisms and efficiencies. Some of the key ways in which vacuum pumps help conserve energy are:
1. Improved Process Efficiency: Vacuum pumps are often used to remove gases and create low-pressure or vacuum conditions in industrial processes. By reducing the pressure, vacuum pumps enable the removal of unwanted gases or vapors, improving the efficiency of the process. For example, in distillation or evaporation processes, vacuum pumps help lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate or distill at lower temperatures. This results in energy savings as less heat is required to achieve the desired separation or concentration.
2. Reduced Energy Consumption: Vacuum pumps are designed to operate efficiently and consume less energy compared to other types of equipment that perform similar functions. Modern vacuum pump designs incorporate advanced technologies, such as variable speed drives, energy-efficient motors, and optimized control systems. These features allow vacuum pumps to adjust their operation based on demand, reducing energy consumption during periods of lower process requirements. By consuming less energy, vacuum pumps contribute to overall energy savings in industrial operations.
3. Leak Detection and Reduction: Vacuum pumps are often used in leak detection processes to identify and locate leaks in systems or equipment. By creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment, vacuum pumps can assess the integrity of a system and identify any sources of leakage. Detecting and repairing leaks promptly helps prevent energy wastage associated with the loss of pressurized fluids or gases. By addressing leaks, vacuum pumps assist in reducing energy losses and improving the overall energy efficiency of the system.
4. Energy Recovery Systems: In some applications, vacuum pumps can be integrated into energy recovery systems. For instance, in certain manufacturing processes, the exhaust gases from vacuum pumps may contain heat or have the potential for energy recovery. By utilizing heat exchangers or other heat recovery systems, the thermal energy from the exhaust gases can be captured and reused to preheat incoming fluids or provide heat to other parts of the process. This energy recovery approach further enhances the overall energy efficiency by utilizing waste heat that would otherwise be lost.
5. System Optimization and Control: Vacuum pumps are often integrated into centralized vacuum systems that serve multiple processes or equipment. These systems allow for better control, monitoring, and optimization of the vacuum generation and distribution. By centralizing the vacuum production and employing intelligent control strategies, energy consumption can be optimized based on the specific process requirements. This ensures that vacuum pumps operate at the most efficient levels, resulting in energy savings.
6. Maintenance and Service: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their optimal performance and energy efficiency. Routine maintenance includes tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection of pump components. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reducing energy consumption. Additionally, prompt repair of any faulty parts or addressing performance issues helps maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevents energy waste.
In summary, vacuum pumps contribute to energy savings through improved process efficiency, reduced energy consumption, leak detection and reduction, integration with energy recovery systems, system optimization and control, as well as proper maintenance and service. By utilizing vacuum pumps efficiently and effectively, industries can minimize energy waste, optimize energy usage, and achieve significant energy savings in various applications and processes.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Laboratories?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are essential tools in laboratory settings as they enable scientists and researchers to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments. These controlled conditions are crucial for various scientific processes and experiments. Here are some key reasons why vacuum pumps are used in laboratories:
1. Evaporation and Distillation: Vacuum pumps are frequently used in laboratory evaporation and distillation processes. By creating a vacuum, they lower the boiling point of liquids, allowing for gentler and more controlled evaporation. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive substances or when precise control over the evaporation process is required.
2. Filtration: Vacuum filtration is a common technique in laboratories for separating solids from liquids or gases. Vacuum pumps create suction, which helps draw the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving the solid particles behind. This method is widely used in processes such as sample preparation, microbiology, and analytical chemistry.
3. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in freeze drying or lyophilization processes. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from a substance while it is in a frozen state, preserving its structure and properties. Vacuum pumps facilitate the sublimation of frozen water directly into vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture under low-pressure conditions.
4. Vacuum Ovens and Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in conjunction with vacuum ovens and chambers to create controlled low-pressure environments for various applications. Vacuum ovens are used for drying heat-sensitive materials, removing solvents, or conducting reactions under reduced pressure. Vacuum chambers are utilized for testing components under simulated space or high-altitude conditions, degassing materials, or studying vacuum-related phenomena.
5. Analytical Instruments: Many laboratory analytical instruments rely on vacuum pumps to function properly. For example, mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, surface analysis equipment, and other analytical instruments often require vacuum conditions to maintain sample integrity and achieve accurate results.
6. Chemistry and Material Science: Vacuum pumps are employed in numerous chemical and material science experiments. They are used for degassing samples, creating controlled atmospheres, conducting reactions under reduced pressure, or studying gas-phase reactions. Vacuum pumps are also used in thin film deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
7. Vacuum Systems for Experiments: In scientific research, vacuum systems are often designed and constructed for specific experiments or applications. These systems can include multiple vacuum pumps, valves, and chambers to create specialized vacuum environments tailored to the requirements of the experiment.
Overall, vacuum pumps are versatile tools that find extensive use in laboratories across various scientific disciplines. They enable researchers to control and manipulate vacuum or low-pressure conditions, facilitating a wide range of processes, experiments, and analyses. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-17
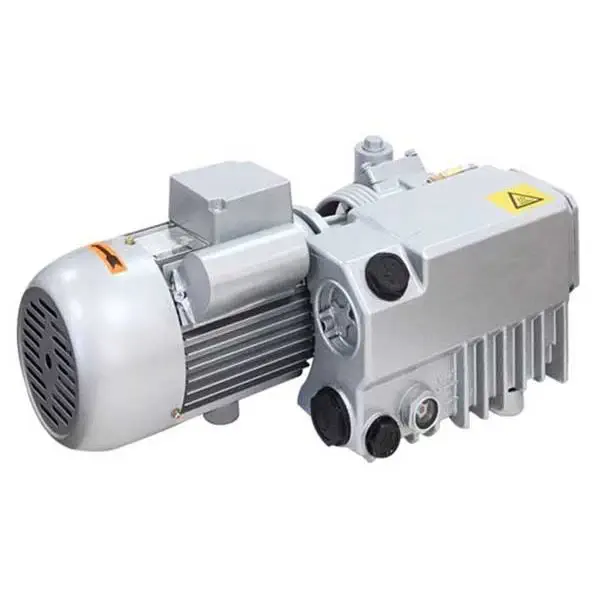
China factory Roots Vacuum Pump Rotary Portable Industrial Mini Vane Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement Best Suppliers DC AC Vacuum Pump vacuum pump belt
Product Description
Roots Vacuum Pump Rotary Portable Industrial Mini Vane Scroll Reciprocating Diaphragm Centrifugal Positive Displacement Best Suppliers DC AC Vacuum Pump
Roots vacuum pump
For many years now Roots vacuum pumps have been well established in the area of vacuum technology. In combination with backing pumps, which compress against the atmosphere, these pumps offer lots of advantages.
Features:
The main advantage of roots vacuum pump is a high pumping speed at the lower inlet pressure with high ultimate vacuum. Since the pump running parts have no contact, such as rotors and the end cover, so the pump performance is stable and long service time. low maintenance cost
Applications:
They’re widely used in vacuum smelting, vacuum welding, vacuum casting, vacuum coating, vacuum drying, vacuum dynamic experiment and chemical pharmaceutical, electric vacuum device manufacturing industries.
In view of the chemical, pharmaceutical and other industries require huge vapor degassing capablity. the sealing structure of roots vacuum pump chamber and the bearing chamber has improved, which greatly reducing the bearing cavity and gear cavity oil emulsification. Thus, roots vacuum pump is more suitable for pumping large quantities of water vapor and solvent with water ring vacuum pump.
company information
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Installation Guide 1-Year Warranty |
| Oil or Not: | Optional |
| Inlet Diam. (mm): | 100/200mm |
| Motor Power (Kw): | 4/7.5 Kw |
| Ultimate Pressure (PA): | 0.05 |
| Samples: |
US$ 999/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

Are there any specific brands or models of AC vacuum pumps that are highly regarded?
Yes, there are several brands and models of AC (air conditioning) vacuum pumps that are highly regarded in the industry for their performance, reliability, and durability. Some of these well-regarded brands and models include:
- 1. Robinair: The Robinair brand offers a range of high-quality vacuum pumps known for their durability and efficiency. The Robinair 15500 and 15800 series pumps are popular choices among HVAC professionals.
- 2. Yellow Jacket: Yellow Jacket vacuum pumps are known for their robust construction and reliable performance. The Yellow Jacket SuperEvac series, including models 93560 and 93580, are commonly used in the HVAC industry.
- 3. JB Industries: JB Industries produces a variety of vacuum pumps suitable for AC system evacuation. The DV-6E and Eliminator series pumps are well-regarded for their performance and longevity.
- 4. CPS Products: CPS offers vacuum pumps designed for HVAC applications, with models like the VP6D and VP8D gaining recognition for their efficiency and durability.
- 5. Fieldpiece: Fieldpiece vacuum pumps, such as the VP85 and VP67, are known for their portability and reliability, making them popular among HVAC technicians.
While these brands and models are often recommended by professionals, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and budget when choosing an AC vacuum pump. Factors like the size of the systems you work on, the frequency of use, and additional features can influence your decision. Reading user reviews and seeking recommendations from experienced HVAC technicians can also help you make an informed choice.

What safety precautions should be taken when using an AC vacuum pump?
When using an AC vacuum pump, it is important to follow proper safety precautions to ensure personal safety and prevent potential hazards. Here’s a detailed explanation of the safety precautions that should be taken when using an AC vacuum pump:
- Read the User Manual: Before operating the AC vacuum pump, carefully read and understand the manufacturer’s user manual and instructions. Familiarize yourself with the specific safety guidelines and recommendations provided by the manufacturer.
- Protective Gear: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as safety glasses, gloves, and closed-toe shoes when using the vacuum pump. PPE helps protect against potential hazards, including eye injuries, chemical exposure, or physical injuries during operation.
- Ventilation: Ensure that the area where the AC vacuum pump is operated has adequate ventilation. Good ventilation helps prevent the buildup of potentially harmful gases, fumes, or vapors that may be generated during the evacuation process.
- Electrical Safety: Follow electrical safety precautions when using the vacuum pump. Ensure that the electrical connections and power supply are in good condition. If the pump is powered by electricity, use grounded outlets and appropriate extension cords as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Secure Placement: Place the AC vacuum pump on a stable and level surface to prevent tipping or falling during operation. Ensure that the pump is securely positioned and cannot be easily knocked over.
- Proper Use: Use the AC vacuum pump according to its intended purpose and within its specified operational limits. Avoid exceeding the recommended vacuum level or operating duration to prevent equipment damage or potential hazards.
- Avoid Overheating: Pay attention to the temperature of the vacuum pump during operation. Some pumps may generate heat, and prolonged use without proper cooling or rest intervals can lead to overheating. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cooling and rest periods, if applicable.
- Inspect Hoses and Connections: Regularly inspect the hoses, fittings, and connections associated with the vacuum pump. Ensure that they are in good condition, free from damage or leaks. Tighten any loose connections to maintain proper vacuum integrity and prevent accidents or injuries.
- Emergency Stop: Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop or shut-off feature of the AC vacuum pump. In case of an emergency or abnormal operation, know how to quickly and safely stop the pump to avoid further risks or damage.
- Training and Experience: Operate the AC vacuum pump only if you have received proper training or have sufficient experience. If you are unfamiliar with its operation or maintenance, seek guidance from a qualified professional or technician.
By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, or equipment damage when using an AC vacuum pump. Safety should always be a priority to ensure a safe working environment and protect both yourself and others involved in the operation.

Can you explain the process of evacuating an AC system with a vacuum pump?
The process of evacuating an AC system with a vacuum pump involves several steps to remove air, moisture, and contaminants from the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process:
- Preparation: Before starting the evacuation process, ensure that the AC system is properly shut off and any electrical power supply is disconnected. It’s also important to have the necessary safety equipment, such as gloves and safety goggles, to protect yourself during the process.
- Connect the Vacuum Pump: Connect one end of the vacuum pump’s intake hose to the intake port of the AC system. Ensure a secure connection, as any leaks can compromise the effectiveness of the evacuation process. The other end of the intake hose is connected to the vacuum pump’s intake port.
- Prepare the Vacuum Pump: Check the oil level in the vacuum pump and ensure it is at the recommended level. If necessary, add or replace the oil according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This step is crucial as proper lubrication ensures the efficient operation of the vacuum pump.
- Open Valves: Open the valves on the AC system that allow access to the refrigerant lines or components. These valves may include service valves, manifold gauge valves, or access valves. By opening these valves, the vacuum pump can create a vacuum in the system and draw out the air and moisture.
- Start the Vacuum Pump: Turn on the vacuum pump using the control panel or switch. The electric motor of the vacuum pump will start, driving the rotation of the impeller or vane assembly.
- Monitor the Vacuum Gauge: Keep an eye on the vacuum gauge connected to the AC system or the vacuum pump. The gauge will display the level of vacuum being created in the system. The target vacuum level will depend on the specific requirements of the AC system and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Evacuation Time: The duration of the evacuation process depends on factors such as the size of the AC system, the level of contamination, and the vacuum pump’s capacity. Typically, the evacuation process can take anywhere from 20 minutes to several hours. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry standards for the recommended evacuation time.
- Leak Testing: After reaching the desired vacuum level, close the valves on the AC system and turn off the vacuum pump. Monitor the vacuum gauge for any pressure rise over a period of time. If the pressure rises, it indicates the presence of leaks in the system, and further troubleshooting and repairs are necessary before proceeding.
- Refrigerant Charging: Once the AC system has been successfully evacuated and passes the leak test, it is ready for refrigerant charging. Follow the appropriate procedures for charging the system with the recommended refrigerant type and quantity.
- Final Checks: After the refrigerant charging process, perform additional checks to ensure the proper operation of the AC system. These checks may include verifying the cooling performance, inspecting for any abnormal noises or vibrations, and confirming that all system components are functioning correctly.
It’s important to note that the process of evacuating an AC system with a vacuum pump should be performed by trained professionals who are familiar with the specific equipment and safety procedures. Improper evacuation can lead to system malfunctions, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards.


editor by Dream 2024-05-17
China high quality Pump Vacuum Pump 2sk-3 Series 7.5kw Water Ring Vacuum Pump manufacturer
Product Description
Product Description
|
Power |
Voltage |
Air volume |
Wind pressure |
Suction pressure |
|
3kw Ring Blower |
380v |
318m³/h |
38kpa |
35kpa |
|
4kw Ring Blower |
380v |
420m³/h |
45kpa |
41kpa |
|
5.5kw Ring Blower |
380v |
500m³/h |
50kpa |
48kpa |
|
7.5kw Ring Blower |
380v |
520m³/h |
56kpa |
51kpa |
1) Beautiful surface and Small dimensions in the die-cast aluminum alloy housing
2) Both 50Hz and 60Hz are available.
3) Dual-usage: Compressor and Vacuum (suction and blow).
4) Electronic motor with IP54 protection and Insulation class F.
5) 100% oil-free and no oily odors.
6) Low noise and libration.
7) Maintenance-free and easy installation.
8) Strong dynamic stability without vibration
9) Pulsation-free discharge
10) Cooler running bearings
11) Longer grease life
12) Suitable for environmental protection
13) Continuous duty
Company Profile
HangZhou CHINAMFG Bao Automation Equipment Co., Ltd.
From China to the world
Diaobao CNC Equipment Co., Ltd. is a company that integrates production, sales, and research and development. It is committed to providing automation equipment manufacturing for global users, and upholds the product development concept of high efficiency, intelligence, environmental protection, and compatibility. Since its establishment, Diaobao CNC has developed rapidly and has 2 standardized intelligent equipment manufacturing bases with a total area of over 10,000 square meters. We are focus on CNC Machine Parts.It is specialized in five-axis engraving machines, vibrating knife cutting machines, woodworking engraving machines, stone engraving machines, advertising engraving machines, mold precision engraving machines, and CNC engraving and milling machines. The products have passed ISO9001 certification and are reliable in quality and complete in variety. They are exported to the Middle East, Africa, South America, and other regions. They operate stably in the woodworking industry, model industry, mold industry, blister industry, packaging industry, clothing industry, automotive interior industry, leather cutting industry, etc. They have a wide range of benchmarking customer examples. Professional independent core research and development team and well-established after-sales technical department truly provide customer-centric service experience.
FAQ
1.About us
We are in HangZhou ZheJiang , which is the hometown of CNC Router. We are focus on CNC Machine Parts.
We’ve been in this business for more than 10 years.
2.What products do we have?
We have many CNC Machine Parts , include Spindle,Inverter,stepper motor,driver,guide rail,sliding block,
rack,gear box,water pump,dust collector,coupling,tool-setter,tool cutter. And so on …
3.How we guarantee the quality of the products?
Each batch of products will pass the test before leaving the factory.
Before delivery, we will check the list 1 by one.
4.Why you should choose us?
We are focus on CNC Router Parts more than 10years. We can provide you with the overall solution, We
can offer you many type CNC products.Just tell us which you need , we will provide you as the best price
and the best quality and service.
5.What’s the payment term?
We normally accept T/T, Western Union, L/C, and Paypal.
6.What about the shipping ?
We support multiple modes of transportation,such as by express,by air,by sea,by rail and so on.
Also can shipping by DHL\FedEx\TNT\UPS\EMS and so on.
We can offer different type transactions: FOB\EXW\FCA\DAP\CIF.
We can also help you to keep other suppliers goods at our warehouse and shipping together.
7.How to place an order?
Just tell us what you need , then we can make a Invoice for you. If all OK , then make the order and we
shipping to you the goods ASAP.
In order to ensure that all products are what you need, we will show you the pictures, drawings, videos
and so on before shipping .
8.What about the delivery time?
We have a large warehouse and most of our goods are in stock.When you have order, we can shipping
the goods fast.
Generally speaking, the time from our warehouse to the forwarder is about 2 days, and then the goods
can be sent by DHL FedEx UPS TNT to you.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Timely After-Sales Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Entrapment Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Samples: |
US$ 500/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Aerospace Sector?
Vacuum pumps indeed have various applications in the aerospace sector. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in several areas of the aerospace industry, supporting various processes and systems. Some of the key applications of vacuum pumps in the aerospace sector include:
1. Space Simulation Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in space simulation chambers to replicate the low-pressure conditions experienced in outer space. These chambers are utilized for testing and validating the performance and functionality of aerospace components and systems under simulated space conditions. Vacuum pumps create and maintain the necessary vacuum environment within these chambers, allowing engineers and scientists to evaluate the behavior and response of aerospace equipment in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Management: In space propulsion systems, vacuum pumps are employed for propellant management. They help in the transfer, circulation, and pressurization of propellants, such as liquid rocket fuels or cryogenic fluids, in both launch vehicles and spacecraft. Vacuum pumps assist in creating the required pressure differentials for propellant flow and control, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of propulsion systems.
3. Environmental Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft. These systems are responsible for maintaining the desired atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and cabin pressure, to ensure the comfort, safety, and well-being of crew members and passengers. Vacuum pumps are used to regulate and control the cabin pressure, facilitating the circulation of fresh air and maintaining the desired air quality within the aircraft or spacecraft.
4. Satellite Technology: Vacuum pumps find numerous applications in satellite technology. They are used in the fabrication and testing of satellite components, such as sensors, detectors, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for thin film deposition, surface treatment, and testing processes, ensuring the performance and reliability of satellite equipment. Additionally, vacuum pumps are employed in satellite propulsion systems to manage propellants and provide thrust for orbital maneuvers.
5. Avionics and Instrumentation: Vacuum pumps are involved in the production and testing of avionics and instrumentation systems used in aerospace applications. They facilitate processes such as thin film deposition, vacuum encapsulation, and vacuum drying, ensuring the integrity and functionality of electronic components and circuitry. Vacuum pumps are also utilized in vacuum leak testing, where they help create a vacuum environment to detect and locate any leaks in aerospace systems and components.
6. High Altitude Testing: Vacuum pumps are used in high altitude testing facilities to simulate the low-pressure conditions encountered at high altitudes. These testing facilities are employed for evaluating the performance and functionality of aerospace equipment, such as engines, materials, and structures, under simulated high altitude conditions. Vacuum pumps create and control the required low-pressure environment, allowing engineers and researchers to assess the behavior and response of aerospace systems in high altitude scenarios.
7. Rocket Engine Testing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in rocket engine testing facilities. They are utilized to evacuate and maintain the vacuum conditions in engine test chambers or nozzles during rocket engine testing. By creating a vacuum environment, these pumps simulate the conditions experienced by rocket engines in the vacuum of space, enabling accurate testing and evaluation of engine performance, thrust levels, and efficiency.
It’s important to note that aerospace applications often require specialized vacuum pumps capable of meeting stringent requirements, such as high reliability, low outgassing, compatibility with propellants or cryogenic fluids, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures.
In summary, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the aerospace sector for a wide range of applications, including space simulation chambers, propellant management, environmental control systems, satellite technology, avionics and instrumentation, high altitude testing, and rocket engine testing. They contribute to the development, testing, and operation of aerospace equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Food Processing?
Yes, vacuum pumps are widely used in food processing for various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in the food processing industry by enabling the creation and maintenance of vacuum or low-pressure environments. They offer several benefits in terms of food preservation, packaging, and processing. Here are some common applications of vacuum pumps in food processing:
1. Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in vacuum packaging processes. Vacuum packaging involves removing air from the packaging container to create a vacuum-sealed environment. This process helps extend the shelf life of food products by inhibiting the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms and reducing oxidation. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the air from the packaging, ensuring a tight seal and maintaining the quality and freshness of the food.
2. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps are essential in freeze drying or lyophilization processes used in food processing. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from food products while they are frozen, preserving their texture, flavor, and nutritional content. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment that allows frozen water to directly sublimate from solid to vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture from the food without causing damage or loss of quality.
3. Vacuum Cooling: Vacuum pumps are utilized in vacuum cooling processes for rapid and efficient cooling of food products. Vacuum cooling involves placing the food in a vacuum chamber and reducing the pressure. This lowers the boiling point of water, facilitating the rapid evaporation of moisture and heat from the food, thereby cooling it quickly. Vacuum cooling helps maintain the freshness, texture, and quality of delicate food items such as fruits, vegetables, and bakery products.
4. Vacuum Concentration: Vacuum pumps are employed in vacuum concentration processes in the food industry. Vacuum concentration involves removing excess moisture from liquid food products to increase their solids content. By creating a vacuum, the boiling point of the liquid is reduced, allowing for gentle evaporation of water while preserving the desired flavors, nutrients, and viscosity of the product. Vacuum concentration is commonly used in the production of juices, sauces, and concentrates.
5. Vacuum Mixing and Deaeration: Vacuum pumps are used in mixing and deaeration processes in food processing. In the production of certain food products such as chocolates, confectioneries, and sauces, vacuum mixing is employed to remove air bubbles, achieve homogeneity, and improve product texture. Vacuum pumps aid in the removal of entrapped air and gases, resulting in smooth and uniform food products.
6. Vacuum Filtration: Vacuum pumps are utilized in food processing for vacuum filtration applications. Vacuum filtration involves separating solids from liquids or gases using a filter medium. Vacuum pumps create suction that draws the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving behind the solid particles. Vacuum filtration is commonly used in processes such as clarifying liquids, removing impurities, and separating solids from liquids in the production of beverages, oils, and dairy products.
7. Marinating and Brining: Vacuum pumps are employed in marinating and brining processes in the food industry. By applying a vacuum to the marinating or brining container, the pressure is reduced, allowing the marinade or brine to penetrate the food more efficiently. Vacuum marinating and brining help enhance flavor absorption, reduce marinating time, and improve the overall taste and texture of the food.
8. Controlled Atmosphere Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in controlled atmosphere packaging (CAP) systems in the food industry. CAP involves modifying the gas composition within food packaging to extend the shelf life and maintain the quality of perishable products. Vacuum pumps aid in the removal of oxygen or other unwanted gases from the package, allowing the introduction of a desired gas mixture that preserves the food’s freshness and inhibits microbial growth.
These are just a few examples of how vacuum pumps are used in food processing. The ability to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments is a valuable asset in preserving food quality, enhancing shelf life, and facilitating various processing techniques in the food industry.


editor by Dream 2024-05-17
China supplier Model 2xz Molecular Sliding Vane Rotary Vacuum Pump vacuum pump belt
Product Description
Product Description
Brief Description of vacuum pump liquid ring
YH500 Diaphragm Vacuum Pump is a kind of variable volume type vacuum pump, and is a new type with excellent functions and high quality after improvement on the basis of learning merits and eliminating shortcoming of similar products at home and abroad. YH500 Diaphragm Vacuum Pump’s rotating speed≥1390r/min; input power≤550W; ultimate vacuum is 700Kpa; volume flow is 40L/min. This pump can be widely used in experiments of vacuum filtration, rotary evaporator, refrigeration, dryness, vacuum concentration and molecular distillation.
Working principle of YH500 diaphragm vacuum pump:
The motor shaft is sheathed with an eccentric wheel, 1 end of the connecting rod is sheathed on the eccentric wheel, and the other end is connected with the soft membrane. With the rotation of the motor to drive the connecting rod for reciprocating motion. The rod is driven diaphragm which fixed on the pump body to do recycle motion, to generate elastic deformation, so that pumping chamber volume changed periodically. In the pump body, there are an inlet and an exhaust valve, inhale when the volume becomes large, exhaust when the volume becomes small, thereby reach the purpose of pumping gas.
Product Features of YH500 Diaphragm Vacuum Pump:
1.There is filtering material in the gas exchange position, thereby ensuring the cleanness of air;
2.Working without medium, so no oil vapor pollution, is the ideal equipment to obtain clean vacuum;
3.New technology and new materials are used in the production process, it is easy to move and work smoothly, thus ensuring the ideal vacuum degree and the higher air flow rate;
4.Using non friction of the film body movement, no heat, no friction loss. Diaphragm uses imported rubber, corrosion resistance, long service life;
5.Pressure adjustable design, can meet a certain range of vacuum and gas flow rate;
6.The bearings use imported classic bearings, smooth running, low noise, high efficiency.
Product Display
Technical Parameter
| Model | YH500 | YH700 |
| Voltage/Hertz | 220V/50Hz | 220V/50Hz |
| Rotating speed | ≥1390r/min | ≥1390r/min |
| Input power | ≤550W | ≤800W |
| Working temperature | 5~40ºC | 5~40ºC |
| Extremely vacuum | 700Kpa | 700Kpa |
| Volume flow | 40L/min | 56L/min |
| Size | 264.5×127×186mm | 262×128×214.5mm |
| Insulation grade | B | B |
Corollary Equipment
1. YH500 diaphragm pump corollary use with freezer dryer to reach vacuum state, it’s an essential corollary equipment in medicine CZPT drying, biology, food industry and agricultural products deep processing.
2. YH500 diaphragm pump corollary use with vacuum drying oven for maintaining vacuum state inside the oven, they mainly applies in powder drying and baking in vacuum condition.
3. YH500 diaphragm pump corollary use with rotary evaporator for vacuum pumping, they are widely used in the concentration, crystallization, drying, separation and solvent recovery in industries as medicine, chemical engineering, biopharmacy, etc..
4. YH500 diaphragm pump corollary use with vacuum filter so as to filtrate vacuum for liquid material, they are ideal vacuum filtration instruments in chemical engineering, medicine, petroleum, papermaking and other areas.
Recommending Styles
Q: Is YH500 diaphragm vacuum pump need media when operate?
A: In the working state, it doesn’t need working medium, so there is no oil vapor pollution.
Q: What’s the maximum vacuum which YH500 vacuum pump liquid ring can achieved?
A: The maximum vacuum is 700Kpa.
Q: Comparing to similar products,what’s the advantage of YH500?
Small size and light weight;
Easy to move, work smoothly;
Strong pumping force, resistance rot cavity, long using life;
No media operation, clean and sanitary, safe and reliable;
Smooth running, low noise, high efficiency.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | ISO9001:2008, CE |
|---|---|
| Voltage: | 220V |
| Material: | Aluminum Alloy |
| Power: | Pneumatic |
| Valve Body Type: | Diaphragm |
| Performance: | Health |
| Samples: |
US$ 460/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|

What Are Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps use air flow as the source of energy. The system is ideal for dewatering wet media, creating filter cakes, and pneumatically moving materials through a pipe. A vacuum pump works through air flow that is moved by differential pressure. The pump’s air flow develops a vacuum in a chamber that is called the vacuum box. As the air flow collects gas at a faster rate than atmospheric pressure, it is considered the “heart” of a vacuum system.
Principles of operation
Vacuum pumps work by reducing the volume of air that moves through them. Depending on the design, there are several different types of vacuum pumps. All of these types operate under the same principles, but have their own special features. Here are some of their most important characteristics. In addition to their capacity, the main differences between these pumps are their manufacturing tolerances, materials of construction, and level of tolerance for chemicals, oil vapor, and vibration.
Vacuum pumps create a partial or low-pressure vacuum by forcing gas molecules from their high-pressure states to their low-pressure states. However, these pumps can only achieve a partial vacuum, and other methods are necessary to reach a higher level of vacuum. As with all pumps, there are several ways to increase the level of a vacuum.
First, consider the type of vacuum you want. This is the most important factor when choosing a vacuum pump. If you need a high level of vacuum, you’ll need a high-quality vacuum pump. High-quality vacuum pumps have a high pressure limit, while ultrahigh-quality pumps are capable of achieving a very low vacuum. As the pressure decreases, the amount of molecules per cubic centimeter decreases and the quality of the vacuum increases.
Positive displacement pumps are best suited for low and medium-pressure systems. But they can’t reach high vacuum, which is why most high-pressure systems use two pumps in tandem. In this case, the positive displacement pump would stall and the other one would be used instead. Similarly, entrapment pumps have higher-pressure limits, so they must be refreshed frequently or exhaust frequently when there is too much gas to capture.
Another important aspect of vacuum pump operation is its speed. The speed of pumping is proportional to the differential pressure across the system. Therefore, the faster the pumping speed, the lower the draining time.
Design
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to generate a vacuum. It can create a low or high vacuum. These pumps are used in the process of oil regeneration and re-refining. The design of a vacuum pump must be compatible with the vacuum. The pump’s mass and speed should be matched.
The design of a vacuum pump is important for many reasons. It should be easy to use and maintain. Vacuum pumps need to be protected from external contamination. For this reason, the oil must be kept clean at all times. Contamination may damage the oil, resulting in pump failure. The pump’s design should include features that will prevent this from happening.
The main objective of a vacuum pump is to remove air and other gases from a chamber. As the pressure of the chamber drops, the amount of molecules that can be removed becomes more difficult. Because of this, industrial and research vacuum systems typically require pumps to operate over a large pressure range. The range is generally between one and 10-6 Torr. A standard vacuum system uses multiple pumps, each covering a portion of the pressure range. These pumps can also be operated in a series to achieve optimal performance.
The design of a vacuum pump can vary depending on the application and the pressure requirement. It should be sized appropriately to ensure that it works properly. There are several different types of pumps, so selecting the right pump is essential to maximizing its efficiency. For example, a slow running vee belt drive rotary vane vacuum pump will have a lower running temperature than a fast-running direct-drive pump.
Performance
The performance of a vacuum pump is an important indicator of its overall condition. It helps determine whether the system is performing optimally and how high the ultimate vacuum level can be achieved. A performance log should be maintained to document variations in pump operating hours and voltage as well as the temperature of the pump’s cooling water and oil. The log should also record any problems with the pump.
There are several ways to increase the performance of a vacuum pump. For example, one way is to decrease the temperature of the working fluid. If the temperature of the fluid is too high, it will lead to a low vacuum. A high temperature will make the vacuum degree of the pump even lower, so heat transfer is an important part of the process.
Nozzles are another major component that impacts the performance of a vacuum pump. Damage or clogging can result in a compromised pumping capacity. These problems can occur due to a number of causes, including excessive noise, leakage, and misassembled parts. Nozzles can also become clogged due to rusting, corrosion, or excess water.
Performance of vacuum pump technology is vital for many industries. It is an integral part of many central production processes. However, it comes with certain expenses, including machines, installations, energy, and maintenance. This makes it essential to understand what to look for when purchasing a vacuum pump. It is important to understand the factors that can influence these factors, as they affect the efficiency of a vacuum pump.
Another important factor in determining the performance of a vacuum pump is throughput. Throughput is a measurement of how many molecules can be pumped per unit of time at a constant temperature. Moreover, throughput can also be used to evaluate volume leak rates and pressure at the vacuum side. In this way, the efficiency of a vacuum pump can be judged by the speed and throughput of its leaks.
Atmospheric pressure
Vacuum pumps work by sucking liquids or air into a container. The amount of vacuum a pump can create is measured in pressure units called atms (atmospheric pressure). The pressure of a vacuum pump is equal to the difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure in the system.
The amount of force produced by air molecules on each other is proportional to the number of impacts. Therefore, the greater the impact, the higher the pressure. In addition, all molecules have the same amount of energy at any temperature. This holds true for both pure and mixture gases. However, lighter molecules will move faster than heavier ones. Nevertheless, the transfer of energy is the same for both.
The difference between atmospheric and gauge pressure is not always straightforward. Some applications use one term to describe the other. While the two concepts are closely related, there are key differences. In most cases, atmospheric pressure is a higher number than gauge pressure. As a result, it can be confusing when choosing a vacuum pump.
One method is to use a U-tube manometer, a compact device that measures the difference between atmospheric pressure and vacuum. This device is commonly used for monitoring vacuum systems. It can measure both negative and positive pressure. In addition, it uses an electronic version of a gauge.
The atmospheric pressure affects the performance of a vacuum pump. When working with porous materials, the pump must overcome leakage. As a result, it must be equipped with enough capacity to compensate for variations in the porosity of the work piece. This is why it is critical to buy a vacuum pump that has a large enough capacity to handle the variation.
Typical application
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications. They generate low and high pressures and are used to evaporate water or gases from various materials. They are also used in petroleum regeneration and re-refining processes. Typical applications of vacuum pumps include: a.
b. Rotary vane pumps are used in a variety of vacuum applications. They are suitable for industrial applications, freeze drying and cabinet making. They use oil as a sealant and coolant, allowing them to perform well in a variety of applications. This makes them ideal for use in a variety of industries.
The pumping rate of the vacuum pump is important. This refers to the volume pumped from a given point at a given rate. The higher the speed, the faster the pump will expel the air. Depending on the gas composition, this number will vary. When choosing a vacuum pump, gas composition and process requirements should be considered.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industries from laboratories to medical facilities. In medical applications, they are used in radiation therapy and radiopharmaceuticals. They are also used in mass spectrometers, which are instruments used to analyze solid, liquid, or surface materials. Vacuum pumps are also used in decorative vacuum coatings and Formula 1 engine components. A trash compactor is another example of using a vacuum pump.
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of applications including water purification and aeration. Vacuum pumps are also used in portable dental equipment and compressors in the dental industry. Vacuum pumps are also used in molds for dental implants. Other common applications for vacuum pumps include soil aeration and air sampling.


editor by Dream 2024-05-17
China wholesaler Portable Oil Free Vacuum Pump for Coffee and Espresso Equipment vacuum pump distributors
Product Description
Product Parameter
|
ITEM NO |
GLE550A2 |
|
Name |
Oil free vacuum pump |
|
Packing |
2 pcs / carton case , 54 pcs / pallet |
|
Weight |
9.0 kg |
|
Dimension |
240*113*200 mm |
|
Installation size |
89*203 mm (4*M6) |
|
Technical Specification |
Voltage : According to your requirements ; Vacuum flow : 100 L/min @-92Kpa : (One-Grade vacuum) 50 L/min @-98Kpa :(Two-Grade vacuum) Power: 400 W ; Noise : ≤51dB(A) ; Speed: 1440rpm / 1700rpm ; Temperature : -5ºC-40ºC |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | on Line Support and Free Spare Parts |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Two Years |
| Lubrication Style: | Oil-free |
| Vacuum Flow: | 100 L/Min @-92kpa : (One-Grade Vacuum) |
| Noise: | ≤51dB(a) |
| Brand Name: | OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 65/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
Basic knowledge of vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a device that draws gas molecules from a sealed volume and maintains a partial vacuum. Its main job is to create a relative vacuum within a given volume or volumes. There are many types of vacuum pumps. This article will describe how they work, their types, and their applications.
How it works
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device that removes gas from a system by applying it to a higher pressure than the surrounding atmosphere. The working principle of the vacuum pump is based on the principle of gas transfer and entrapment. Vacuum pumps can be classified according to their vacuum level and the number of molecules that can be removed per cubic centimeter of space. In medium to high vacuum, viscous flow occurs when gas molecules collide with each other. Increasing the vacuum causes molecular or transitional flow.
A vacuum pump has several components that make it a versatile tool. One of the main components is the motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator. The rotor and stator contain coils that generate a magnetic field when excited. Both parts must be mounted on a base that supports the weight of the pump. There is also an oil drain that circulates oil throughout the system for lubrication and cooling purposes.
Another type of vacuum pump is the liquid ring vacuum pump. It works by positioning the impeller above or below the blades. Liquid ring pumps can also adjust the speed of the impeller. However, if you plan to use this type of pump, it is advisable to consult a specialist.
Vacuum pumps work by moving gas molecules to areas of higher or lower pressure. As the pressure decreases, the removal of the molecules becomes more difficult. Industrial vacuum systems require pumps capable of operating in the 1 to 10-6 Torr range.
Type
There are different types of vacuum pumps. They are used in many different applications, such as laboratories. The main purpose of these pumps is to remove air or gas molecules from the vacuum chamber. Different types of pumps use different techniques to achieve this. Some types of pumps use positive displacement, while others use liquid ring, molecular transfer, and entrapment techniques.
Some of these pumps are used in industrial processes, including making vacuum tubes, CRTs, electric lights, and semiconductor processing. They are also used in motor vehicles to power hydraulic components and aircraft. The gyroscope is usually controlled by these pumps. In some cases, they are also used in medical settings.
How a vacuum pump works depends on the type of gas being pumped. There are three main types: positive displacement, negative displacement, and momentum transfer. Depending on the type of lubrication, these principles can be further divided into different types of pumps. For example, dry vacuum pumps are less sensitive to gases and vapors.
Another type of vacuum pump is called a rotary vane pump. This type of pump has two main components, the rotor and the vacuum chamber. These pumps work by rotating moving parts against the pump casing. The mating surfaces of rotary pumps are designed with very small clearances to prevent fluid leakage to the low pressure side. They are suitable for vacuum applications requiring low pulsation and high continuous flow. However, they are not suitable for use with grinding media.
There are many types of vacuum pumps and it is important to choose the right one for your application. The type of pump depends on the needs and purpose of the system. The larger ones can work continuously, and the smaller ones are more suitable for intermittent use. 
Apply
Vacuum pumps are used in a variety of industrial and scientific processes. For example, they are used in the production of vacuum tubes, CRTs, and electric lamps. They are also used in semiconductor processing. Vacuum pumps are also used as mechanical supports for other equipment. For example, there may be multiple vacuum pumps on the engine of a motor vehicle that powers the hydraulic components of an aircraft. In addition, they are often used in fusion research.
The most common type of vacuum pump used in the laboratory is the rotary vane pump. It works by directing airflow through a series of rotating blades in a circular housing. As the blades pass through the casing, they remove gas from the cavity and create a vacuum. Rotary pumps are usually single or double-stage and can handle pressures between 10 and 6 bar. It also has a high pumping speed.
Vacuum pumps are also used to fabricate solar cells on wafers. This involves a range of processes including doping, diffusion, dry etching, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition, and bulk powder generation. These applications depend on the type of vacuum pump used in the process, and the vacuum pump chosen should be designed for the environment.
While there are several types of vacuum pumps available, their basic working principles remain the same. Each has different functions and capacities, depending on the type of vacuum. Generally divided into positive displacement pump, rotary vane pump, liquid ring pump, and molecular delivery pump.
Maintenance
The party responsible for general maintenance and repairs is the Principal Investigator (PI). Agknxs must be followed and approved by the PI and other relevant laboratory personnel. The Agknx provides guidelines for routine maintenance of vacuum pump equipment. Agknxs are not intended to replace detailed routine inspections of vacuum pump equipment, which should be performed by certified/qualified service personnel. If the device fails, the user should contact PI or RP for assistance.
First, check the vacuum pump for any loose parts. Make sure the inlet and outlet pressure gauges are open. When the proper pressure is shown, open the gate valve. Also, check the vacuum pump head and flow. Flow and head should be within the range indicated on the label. Bearing temperature should be within 35°F and maximum temperature should not exceed 80°F. The vacuum pump bushing should be replaced when it is severely worn.
If the vacuum pump has experienced several abnormal operating conditions, a performance test should be performed. Results should be compared to reference values to identify abnormalities. To avoid premature pump failure, a systematic approach to predictive maintenance is essential. This is a relatively new area in the semiconductor industry, but leading semiconductor companies and major vacuum pump suppliers have yet to develop a consistent approach.
A simplified pump-down test method is proposed to evaluate the performance of vacuum pumps. The method includes simulated aeration field tests and four pump performance indicators. Performance metrics are evaluated under gas-loaded, idle, and gas-load-dependent test conditions. 
Cost
The total cost of a vacuum pump consists of two main components: the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. The latter is the most expensive component, as it consumes about four to five times the initial investment. Therefore, choosing a more energy-efficient model is a good way to reduce the total system cost and payback period.
The initial cost of a vacuum pump is about $786. Oil-lubricated rotary vane pumps are the cheapest, while oil-free rotary vane pumps are slightly more expensive. Non-contact pumps also cost slightly more. The cost of a vacuum pump is not high, but it is a factor that needs careful consideration.
When choosing a vacuum pump, it is important to consider the type of gas being pumped. Some pumps are only suitable for pumping air, while others are designed to pump helium. Oil-free air has a different pumping rate profile than air. Therefore, you need to consider the characteristics of the medium to ensure that the pump meets your requirements. The cost of a vacuum pump can be much higher than the purchase price, as the daily running and maintenance costs can be much higher.
Lubricated vacuum pumps tend to be more durable and less expensive, but they may require more maintenance. Maintenance costs will depend on the type of gas that needs to be pumped. Lighter gases need to be pumped slowly, while heavier gases need to be pumped faster. The maintenance level of a vacuum pump also depends on how often it needs to be lubricated.
Diaphragm vacuum pumps require regular maintenance and oil changes. The oil in the diaphragm pump should be changed every 3000 hours of use. The pump is also resistant to chemicals and corrosion. Therefore, it can be used in acidic and viscous products.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China factory Mini Diaphragm Brushless DC Air 6V 12V 24V Solvent and UV-Curable Ink Printers Vacuum Pump vacuum pump diy
Product Description
Micro Diaphragm Liquid Pump (TF30A Series ink pump)
The use of chemically resistant materials such as PTFE(TFM), FPM, FFPM, CHINAMFG or other material combinations for the parts which come in contact with the liquid allows almost all neutral or corrosive inks to be pumped:
♦ UV ink ♦ Solvent based ink ♦ Oil based ink ♦ Water based ink ♦ MEK ink etc.
Motor is to a pump what heart is to a person. Compared with (some other brand) markets common pumps, TOPSFLO is featured with the following advantages.
♦ Longer Lifetime
♦ Lower noise, more quiet
♦ Less electromagnetic interference
Equiped with anti-electromagnetic interference capacitors, Topsflo pumps cause little interference to your facility.
♦ Less temperature rise
Are you bothered if pump gets heat soon when it’s working in your facility? Topsflo adopts the most advanced technology as KNF does, the pump won’t get much heat during working,especially outside controller models.
| Model | Rated voltage | No-load current | Max Head | Max Vacuum | Max flow | Lifetime |
| (VDC) | (A) | (M) | (KPa) | (L/min) | (hrs) | |
| TF30A-A | 6/12/24 | 0.4/0.24/0.15 | ≥10M | -70KPa | water : 0.4 | 3,000 |
| gas : 4 | ||||||
| TF30A-C | 6/12/24 | 0.4/0.24/0.15 | ≥10M | -70KPa | water : 0.4 | 15,000 |
| gas : 4 | ||||||
| TF30A-D | 6/12/24 | 0.4/0.24/0.15 | ≥10M | -70KPa | water : 0.4 | 15,000 |
| gas : 4 | ||||||
| TF30B-H | 6/12/24 | 0.24/0.15 | ≥10M | -60KPa | water : 0.35 | 10,000 |
| gas : 4.5 |
1.Excellent Materials Suitable for Various Ink
• Ink types we can handle include UV cured, titanium dioxide pigmented, silver and other metal particles,FDA, security, in addition to the more traditional water, and solvent based inks.
• For corrosive inks, choose among wetted parts of Nylon, PTFE, PVDF, peroxide-cured EPDM, FFPM, FPM, PP, PPS, 316 stainless steel and many others.
♦ UV ink ♦ Solvent based ink ♦ Oil based ink ♦ Water based ink ♦ MEK ink etc.
TOPS INDUSTRY AND TECHNOLOGY CO., LIMITED started in 2005, is the world’s leading supplier of micro
pump solutions, and won the “National High-tech Enterprise”. The company is mainly engaged in the research and development and manufacture of miniature brushless DC
pumps and miniature diaphragm pumps. 80% of the products are exported to high-end markets in Europe and
America, and are mainly used in water heaters, small household appliances, water heating mattresses, medical equipment, smart toilets, chiller, pinter,fast ev charger,automobilecirculation systems, etc. The company has always been known for its high quality and high batch consistency, and has established solid and good cooperative relations with many world-renowned brands, such as: Tesla, Whirlpool, Flextronics, Kohler, GE, Roca, KTM, Geberit, etc.
Get more detail, please contact us ! /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | .. |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | .. |
| Certification: | RoHS, CE |
| Voltage: | 24V |
| Power: | Electric |
| Valve Body Type: | Diaphragm |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Laboratories?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are essential tools in laboratory settings as they enable scientists and researchers to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments. These controlled conditions are crucial for various scientific processes and experiments. Here are some key reasons why vacuum pumps are used in laboratories:
1. Evaporation and Distillation: Vacuum pumps are frequently used in laboratory evaporation and distillation processes. By creating a vacuum, they lower the boiling point of liquids, allowing for gentler and more controlled evaporation. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive substances or when precise control over the evaporation process is required.
2. Filtration: Vacuum filtration is a common technique in laboratories for separating solids from liquids or gases. Vacuum pumps create suction, which helps draw the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving the solid particles behind. This method is widely used in processes such as sample preparation, microbiology, and analytical chemistry.
3. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in freeze drying or lyophilization processes. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from a substance while it is in a frozen state, preserving its structure and properties. Vacuum pumps facilitate the sublimation of frozen water directly into vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture under low-pressure conditions.
4. Vacuum Ovens and Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in conjunction with vacuum ovens and chambers to create controlled low-pressure environments for various applications. Vacuum ovens are used for drying heat-sensitive materials, removing solvents, or conducting reactions under reduced pressure. Vacuum chambers are utilized for testing components under simulated space or high-altitude conditions, degassing materials, or studying vacuum-related phenomena.
5. Analytical Instruments: Many laboratory analytical instruments rely on vacuum pumps to function properly. For example, mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, surface analysis equipment, and other analytical instruments often require vacuum conditions to maintain sample integrity and achieve accurate results.
6. Chemistry and Material Science: Vacuum pumps are employed in numerous chemical and material science experiments. They are used for degassing samples, creating controlled atmospheres, conducting reactions under reduced pressure, or studying gas-phase reactions. Vacuum pumps are also used in thin film deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
7. Vacuum Systems for Experiments: In scientific research, vacuum systems are often designed and constructed for specific experiments or applications. These systems can include multiple vacuum pumps, valves, and chambers to create specialized vacuum environments tailored to the requirements of the experiment.
Overall, vacuum pumps are versatile tools that find extensive use in laboratories across various scientific disciplines. They enable researchers to control and manipulate vacuum or low-pressure conditions, facilitating a wide range of processes, experiments, and analyses. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China high quality Low Energy Oilless Vacuum Pump for Leak Detection vacuum pump ac system
Product Description
Product Parameter
| NOTE: All test values are nominal and for reference only. They are not guaranteed maximum or minimum limits, nor do they imply mean or median. | |
| Model Number | ZGK-120 |
| Performance Data | |
| Head configuration | Pressure parallel flow |
| Nominal voltage/frequency | 220V/50HZ |
| Max. Current | 2.3A |
| Max. Power | 480W |
| Max. Flow | 120L/MIN |
| Max. Vacuum | -90Kpa |
| Speed at rated load | 1400RPM |
| Noise | <57dB |
| Max.Pressure restart | 0 PSI |
| Electrical Data | |
| Motor type[Capacitance] | P.S.C(12uF) |
| Motor insulation class | B |
| Thermal switch[Open temperature] | Thermally protected(145°C) |
| Line lead wire color,gauge | Brown(hot),blue(neutral),18AWG |
| Capacitor lead wire color,gauge | Black,black,18 AWG |
| General Data | |
| Operating ambient air temperature | 50° to 104°F(10° to 40°C) |
| Safety certification | ETL |
| Dimension(LXWXH) | 242X124X184 MM |
| Installation size | 203X88.9 MM |
| Net weight | 8.5KG |
| Application | Surgical aspirator,Cleaning, Disinfection etc. |
Product Application
Our manufacturing process
Our Service
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Air Flow: | 120 L/Min |
|---|---|
| Vacuum: | -90kpa |
| Noise: | ≤57dB(a) |
| Brand Name: | OEM |
| Voltage: | 220V 50Hz |
| Power Source: | AC Power |
| Samples: |
US$ 120/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
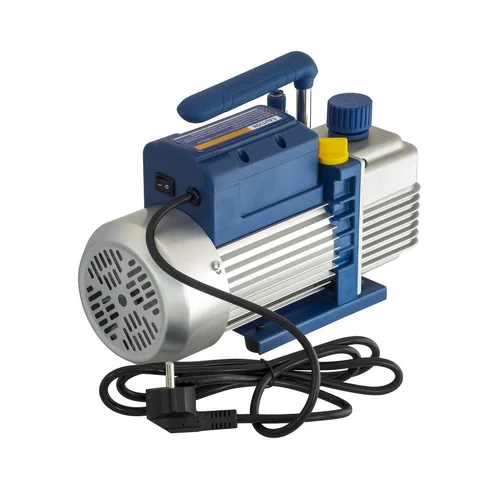

What are the signs that indicate the need for vacuuming an AC system?
Vacuuming an AC (air conditioning) system is essential to ensure its proper functioning and efficiency. Several signs indicate the need for vacuuming an AC system:
- 1. Insufficient Cooling: If the AC system is not cooling your space as effectively as it used to, it may have air or moisture trapped inside, reducing its cooling capacity.
- 2. Ice Formation: Ice forming on the evaporator or refrigerant lines can be a sign of moisture or air in the system. Vacuuming can help remove these contaminants and prevent ice buildup.
- 3. Frequent Repairs: If your AC system requires frequent repairs, it may be due to moisture and contaminants compromising its components. Evacuating the system can reduce the need for repairs.
- 4. Long System Shutdown: If the AC system has been turned off for an extended period, especially in humid conditions, moisture may have entered the system. Vacuuming is crucial to remove this moisture before restarting the system.
- 5. Odors: Unpleasant odors coming from the AC vents can be a sign of microbial growth due to moisture. Vacuuming can help eliminate the moisture and improve air quality.
- 6. Inconsistent Temperatures: If some areas of your space are significantly warmer or colder than others, it could be due to moisture or air affecting the refrigerant flow. Vacuuming can restore uniform cooling.
- 7. System Contamination: Contaminants such as debris, oil, or refrigerant oil can enter the AC system during installation or repair. Vacuuming can remove these contaminants, preventing damage and maintaining system efficiency.
It’s important to note that proper vacuuming should be performed by trained HVAC technicians using appropriate equipment. Attempting to vacuum the AC system without the necessary knowledge and tools can lead to damage or improper evacuation. Regular maintenance, including vacuuming, can prolong the life of your AC system and ensure optimal performance.

What are the common uses of AC vacuum pumps in HVAC systems?
AC vacuum pumps play a crucial role in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, serving various purposes to ensure efficient and reliable operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of the common uses of AC vacuum pumps in HVAC systems:
- Evacuating and Charging Refrigerant: One of the primary uses of AC vacuum pumps in HVAC systems is to evacuate air and moisture from the refrigerant lines and components. Prior to charging the system with refrigerant, the vacuum pump creates a vacuum, removing any non-condensable gases, moisture, and contaminants. This process helps prevent system malfunctions, ensures proper refrigerant flow, and improves overall system performance.
- Leak Testing: AC vacuum pumps are used to perform leak testing in HVAC systems. After the evacuation process, the vacuum pump isolates the system and monitors the pressure. If the pressure rises during the monitoring period, it indicates the presence of leaks. This allows HVAC technicians to identify and repair any leaks before charging the system with refrigerant.
- Brazing and Soldering: During HVAC system installation or repair, brazing or soldering may be required to join refrigerant lines or components. AC vacuum pumps are used to create a vacuum in the lines before brazing or soldering. This removes any contaminants or moisture, ensuring clean and reliable joints that prevent leaks and maintain system efficiency.
- System Maintenance and Service: HVAC systems require periodic maintenance and service to ensure optimal performance. AC vacuum pumps are used to evacuate refrigerant when components need to be replaced or repaired. This prevents refrigerant leaks and contamination during the maintenance process, allowing for efficient and safe servicing of the system.
- Recovery of Refrigerant: In situations where HVAC systems are being decommissioned or refrigerant needs to be recovered for environmental reasons, AC vacuum pumps are used to evacuate and recover the refrigerant from the system. This process helps prevent the release of refrigerants into the atmosphere, which can contribute to ozone depletion or global warming.
AC vacuum pumps are an essential tool in HVAC systems, enabling proper evacuation, leak testing, brazing, system maintenance, and refrigerant recovery. Their use ensures the integrity, efficiency, and reliability of HVAC systems, promoting optimal performance and environmental responsibility.

How do you choose the right AC vacuum pump for your needs?
Choosing the right AC vacuum pump for your needs requires considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your specific requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the considerations for selecting the right AC vacuum pump:
- Vacuum Level: Determine the vacuum level required for your application. Different AC systems or processes may have specific vacuum level requirements. Ensure that the vacuum pump you choose is capable of achieving and maintaining the desired vacuum level.
- Pump Capacity: Consider the pumping capacity or speed of the vacuum pump. The pump capacity is typically measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM) or liters per minute (LPM). Choose a pump with a capacity that matches the size and volume of the AC system you will be evacuating. A larger system may require a pump with a higher pumping capacity.
- Power Source: Determine the available power source for the vacuum pump. AC vacuum pumps are available in different power options, such as 110V or 220V. Ensure that the power source matches the electrical specifications of your facility or the power outlets available for operation.
- Oil or Oil-Free: Decide whether you prefer an oil-lubricated vacuum pump or an oil-free pump. Oil-lubricated pumps generally offer higher vacuum levels and are suitable for more demanding applications. However, they require regular maintenance, such as oil changes, and may not be suitable for applications where oil contamination is a concern. Oil-free pumps are low maintenance and suitable for applications where oil contamination is not acceptable.
- Portability and Size: Consider the portability and size of the vacuum pump. If you require mobility or need to transport the pump to different locations, choose a lightweight and compact model. However, if the pump will be stationary in a workshop or facility, a larger and more robust pump may be appropriate.
- Quality and Durability: Select a vacuum pump from a reputable manufacturer known for producing high-quality and durable equipment. Read customer reviews, check product specifications, and consider the warranty provided by the manufacturer. A reliable vacuum pump ensures long-term performance and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
- Price and Budget: Determine your budget for the vacuum pump. Consider the features, specifications, and performance requirements within your budget range. It’s important to strike a balance between cost and quality to ensure you get a pump that meets your needs without compromising on reliability and performance.
- Additional Features: Consider any additional features or accessories that may be beneficial for your specific application. Some vacuum pumps may include features such as built-in gauges, digital displays, or automatic shut-off mechanisms. These features can enhance convenience, monitoring capabilities, and safety during the evacuation process.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose an AC vacuum pump that matches your specific needs and ensures efficient and effective evacuation of your AC systems or other applications that require vacuum generation.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China factory Reliable and Cost-Effective Hospital Vacuum Pump Tsurumi Pump at Reasonable Price vacuum pump oil near me
Product Description
Application scope and characteristics:
Greentech International (Xihu (West Lake) Dis.) Co., Ltd is the professional vacuum pump supplier. 2BE1 series water ring vacuum pumps and compressors are the products with high efficiency and economic power, which are manufactured by our company integrating with the advanced technology of the imported products from Germany.
These series products adopt CHINAMFG and single action structure and have many advantages, such as, compact structure, convenient maintenance, reliable running, high efficiency and economic power.
The main characteristics of 2BE1 series products:
All the bearings are the imported products with the brand name of CHINAMFG orNTN for ensuring the precise orientation and the high stability during the working of the pump.
The material of the impeller is QT400 nodular iron or stainless steel for ensuring the stability when the pump works under the rigorous condition and can extend the lifetime of the pump.
The casing is made of steel or stainless steel plates to extend the lifetime of the 2BE1 series pumps.
The shaft bushing is made of stainless steel to improve the lifetime of the pump 5 times than the normal material.
The V-belt pulley (when the pump is driven by the belt) is used the high precise pulley with taper bushing to keep the reliability of the pump and extend its life. And it is also easy to mantle and dismantle.
The coupling is used to drive the pump directly. The flexible part connecting the 2 half coupling is made of polyurethane that makes the pump more reliable.
The unique design to set the separator above the pump saves the space and decreases the noise efficiently.
All the parts are cast by the resin sands that make the pump surface very smooth. It is not necessary to cover the surface of the pumps with putty and gives out the heat efficiently.
The mechanical seals (optional) are used the imported products to avoid the leakage when the pump works for a long time.
| Type | Speed (Drive type) r/min |
Shaft power kW |
Motor power kW |
Motor type |
Limited vacuum mbar |
Weight (Whole set) kg |
||
| Suction capacity | ||||||||
| m 3 /h | m 3 /min | |||||||
| 2BE1 151-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
10.8 7.2 9.2 13.2 14.8 |
15 11 11 15 18.5 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
405 300 360 445 470 |
6.8 5.0 6.0 7.4 7.8 |
469 428 444 469 503 |
| 2BE1 152-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
12.5 8.3 10.5 15.0 17.2 |
15 11 15 18.5 22 |
Y160L-4 Y160M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
465 340 415 510 535 |
7.8 5.7 6.9 8.5 8.9 |
481 437 481 515 533 |
| 2BE1 153-0 | 1450(D) 1100(V) 1300(V) 1625(V) 1750(V) |
16.3 10.6 13.6 19.6 22.3 |
18.5 15 18.5 22 30 |
Y180M-4 Y160L-4 Y180M-4 Y180L-4 Y200L-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
600 445 540 660 700 |
10.0 7.4 9.0 11.0 11.7 |
533 480 533 551 601 |
| 2BE1 202-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(v) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
17 14 16 22 25 30 |
22 18.5 18.5 30 30 37 |
Y200L2-6 Y180M-4 Y180M-4 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
760 590 670 850 890 950 |
12.7 9.8 11.2 14.2 14.8 15.8 |
875 850 850 940 945 995 |
| 2BE1 203-0 | 970(D) 790(V) 880(V) 1100(V) 1170(V) 1300(V) |
27 20 23 33 37 45 |
37 30 30 45 45 55 |
Y250M-6 Y200L-4 Y200L-4 Y225M-4 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1120 880 1000 1270 1320 1400 |
18.7 14.7 16.7 21.2 22.0 23.3 |
1065 995 995 1080 1085 1170 |
| 2BE1 252-0 | 740(D) 558(V) 660(V) 832(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
38 26 31.8 49 54 60 |
45 30 37 55 75 75 |
Y280M-8 Y200L-4 Y225S-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
1700 1200 1500 1850 2000 2100 |
28.3 20.0 25.0 30.8 33.3 35.0 |
1693 1460 1515 1645 1805 1805 |
| 2BE1 253-0 | 740(D) 560(V) 660(V) 740(V) 792(V) 833(V) 885(V) 938(V) |
54 37 45 54 60 68 77 86 |
75 45 55 75 75 90 90 110 |
Y315M-8 Y225M-4 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
2450 1750 2140 2450 2560 2700 2870 3571 |
40.8 29.2 35.7 40.8 42.7 45.0 47.8 50.3 |
2215 1695 1785 1945 1945 2055 2060 2295 |
| 2BE1 303-0 | 740(D) 590(D) 466(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
98 65 48 54 64 78 99 |
110 75 55 75 75 90 132 |
Y315L2-8 Y315L2-10 Y250M-4 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315M-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
4000 3200 2500 2800 3100 3580 4000 |
66.7 53.3 41.7 46.7 51.7 59.7 66.7 |
3200 3200 2645 2805 2810 2925 3290 |
| 2BE1 305-1 2BE1 306-1 |
740(D) 590(D) 490(V) 521(V) 583(V) 657(V) 743(V) |
102 70 55 59 68 84 103 |
132 90 75 75 90 110 132 |
Y355M1-8 Y355M1-10 Y280S-4 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
4650 3750 3150 3320 3700 4130 4650 |
77.5 62.5 52.5 55.3 61.2 68.8 77.5 |
3800 3800 2950 3000 3100 3300 3450 |
| 2BE1 353-0 | 590(D) 390(V) 415(V) 464(V) 520(V) 585(V) 620(V) 660(V) |
121 65 70 81 97 121 133 152 |
160 75 90 110 132 160 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280S-4 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5300 3580 3700 4100 4620 5200 5500 5850 |
88.3 59.7 61.7 68.3 77.0 86.7 91.7 97.5 |
4750 3560 3665 3905 4040 4100 4100 4240 |
| 2BE1 355-1 2BE1 356-1 |
590(D) 390(V) 435(V) 464(V) 520(V) 555(V) 585(V) 620(V) |
130 75 86 90 102 115 130 145 |
160 90 110 110 132 132 160 185 |
Y355L2-10 Y280M-4 Y315S-4 Y315S-4 Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6200 4180 4600 4850 5450 5800 6100 6350 |
103.3 69.7 76.7 80.8 90.8 98.3 101.7 105.8 |
5000 3920 4150 4160 4290 4300 4350 4450 |
| 2BE1 403-0 | 330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
97 110 131 160 203 234 |
132 132 160 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
33mbar (-0.098MPa) |
5160 5700 6470 7380 8100 8600 |
86.0 95.0 107.8 123.0 135.0 143.3 |
5860 5870 5950 6190 6630 6800 |
| 2BE1 405-1 2BE1 406-1 |
330(V) 372(V) 420(V) 472(V) 530(V) 565(V) |
100 118 140 170 206 235 |
132 160 185 200 250 280 |
Y315M-4 Y315L1-4 Y315L2-4 Y315L2-4 Y355M2-4 Y355L1-4 |
160mbar (-0.085MPa) |
6000 6700 7500 8350 9450 15710 |
100.0 111.7 125.0 139.2 157.5 168.3 |
5980 6070 6200 6310 6750 6920 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
|---|---|
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Work Function: | Pre-Suction Pump |
| Working Conditions: | Wet |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used for Leak Detection?
Yes, vacuum pumps can be used for leak detection purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Leak detection is a critical task in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and HVAC. It involves identifying and locating leaks in a system or component that may result in the loss of fluids, gases, or pressure. Vacuum pumps can play a significant role in leak detection processes by creating a low-pressure environment and facilitating the detection of leaks through various methods.
Here are some ways in which vacuum pumps can be used for leak detection:
1. Vacuum Decay Method: The vacuum decay method is a common technique used for leak detection. It involves creating a vacuum in a sealed system or component using a vacuum pump and monitoring the pressure change over time. If there is a leak present, the pressure will gradually increase due to the ingress of air or gas. By measuring the rate of pressure rise, the location and size of the leak can be estimated. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the system and establish the initial vacuum required for the test.
2. Bubble Testing: Bubble testing is a simple and visual method for detecting leaks. In this method, the component or system being tested is pressurized with a gas, and then immersed in a liquid, typically soapy water. If there is a leak, the gas escaping from the component will form bubbles in the liquid, indicating the presence and location of the leak. Vacuum pumps can be used to create a pressure differential that forces gas out of the leak, making it easier to detect the bubbles.
3. Helium Leak Detection: Helium leak detection is a highly sensitive method used to locate extremely small leaks. Helium, being a small atom, can easily penetrate small openings and leaks. In this method, the system or component is pressurized with helium gas, and a vacuum pump is used to evacuate the surrounding area. A helium leak detector is then used to sniff or scan the area for the presence of helium, indicating the location of the leak. Vacuum pumps are essential for creating the low-pressure environment required for this method and ensuring accurate detection.
4. Pressure Change Testing: Vacuum pumps can also be used in pressure change testing for leak detection. This method involves pressurizing a system or component and then isolating it from the pressure source. The pressure is monitored over time, and any significant pressure drop indicates the presence of a leak. Vacuum pumps can be used to evacuate the system after pressurization, returning it to atmospheric pressure for comparison or retesting.
5. Mass Spectrometer Leak Detection: Mass spectrometer leak detection is a highly sensitive and precise method used to identify and quantify leaks. It involves introducing a tracer gas, usually helium, into the system or component being tested. A vacuum pump is used to evacuate the surrounding area, and a mass spectrometer is employed to analyze the gas samples for the presence of the tracer gas. This method allows for accurate detection and quantification of leaks down to very low levels. Vacuum pumps are crucial for creating the necessary vacuum conditions and ensuring reliable results.
In summary, vacuum pumps can be effectively used for leak detection purposes. They facilitate various leak detection methods such as vacuum decay, bubble testing, helium leak detection, pressure change testing, and mass spectrometer leak detection. Vacuum pumps create the required low-pressure environment, assist in evacuating the system or component being tested, and enable accurate and reliable leak detection. The choice of vacuum pump depends on the specific requirements of the leak detection method and the sensitivity needed for the application.

Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in Laboratories?
Yes, vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories for a wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are essential tools in laboratory settings as they enable scientists and researchers to create and control vacuum or low-pressure environments. These controlled conditions are crucial for various scientific processes and experiments. Here are some key reasons why vacuum pumps are used in laboratories:
1. Evaporation and Distillation: Vacuum pumps are frequently used in laboratory evaporation and distillation processes. By creating a vacuum, they lower the boiling point of liquids, allowing for gentler and more controlled evaporation. This is particularly useful for heat-sensitive substances or when precise control over the evaporation process is required.
2. Filtration: Vacuum filtration is a common technique in laboratories for separating solids from liquids or gases. Vacuum pumps create suction, which helps draw the liquid or gas through the filter, leaving the solid particles behind. This method is widely used in processes such as sample preparation, microbiology, and analytical chemistry.
3. Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in freeze drying or lyophilization processes. Freeze drying involves removing moisture from a substance while it is in a frozen state, preserving its structure and properties. Vacuum pumps facilitate the sublimation of frozen water directly into vapor, resulting in the removal of moisture under low-pressure conditions.
4. Vacuum Ovens and Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in conjunction with vacuum ovens and chambers to create controlled low-pressure environments for various applications. Vacuum ovens are used for drying heat-sensitive materials, removing solvents, or conducting reactions under reduced pressure. Vacuum chambers are utilized for testing components under simulated space or high-altitude conditions, degassing materials, or studying vacuum-related phenomena.
5. Analytical Instruments: Many laboratory analytical instruments rely on vacuum pumps to function properly. For example, mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, surface analysis equipment, and other analytical instruments often require vacuum conditions to maintain sample integrity and achieve accurate results.
6. Chemistry and Material Science: Vacuum pumps are employed in numerous chemical and material science experiments. They are used for degassing samples, creating controlled atmospheres, conducting reactions under reduced pressure, or studying gas-phase reactions. Vacuum pumps are also used in thin film deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
7. Vacuum Systems for Experiments: In scientific research, vacuum systems are often designed and constructed for specific experiments or applications. These systems can include multiple vacuum pumps, valves, and chambers to create specialized vacuum environments tailored to the requirements of the experiment.
Overall, vacuum pumps are versatile tools that find extensive use in laboratories across various scientific disciplines. They enable researchers to control and manipulate vacuum or low-pressure conditions, facilitating a wide range of processes, experiments, and analyses. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as required vacuum level, flow rate, chemical compatibility, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China high quality Mini Vacuum Pump vacuum pump belt
Product Description
Mini Vacuum Pump
♦ 16000M2 modern factory with its own physical property rights, ESD anti-static control dust free workshop,
100+ sets of professional imported equipment
♦ 4 major professional and precision laboratories that meet the CNAS national laboratory accreditation standards
♦ More than 50 patents in the micro water pump industry, strong research and development strength, and master advanced industry technology
♦ Complete certification, passed CE, ROHS, REACH, WRAS, Food Grade and other certification
Remarks:
– We are high-end Micro DC pumps manufacturer. Can provide customized services
– If you are interested in our products, pls feel free to contact us
Our Micro Diaphragm Pumps are available with a choice of 4 different drive motors.
A- Premium duty brush DC motor
lifetime 3,000hours,longer endurance lifetime than other normal DC membrane pump
B- Economical brush DC motor
lifetime:1,500hours
C- Coreless Brushless DC Motor
A brushless electronically commutated dc motor (electronics integrated in motor), the motor runs vibration and spark free, almost silently, is very dynamic and extremely durable, ideal life-time 15000 hours
D- Coreless Brushless DC motor with outer controller
With all advantages of coreless brushless DC motor, ideal life-time 15000 hours, and outer controller can realize more control functions of PWM or 0 -5V speed adjustment, brake, ~ instant starting work
H- Brushless DC Motor
Long lifetime 10000hour
Product Specification
| Model | TM30A-A | TM30A-B | TM30A-C | TM30A-D |
| Motor type |
A–high performance Brush motor |
B–Brush motor | C–Brushless motor | D–Brushless motor |
| Pump Assembly Rated Life | 3000hour | 1000hour | 15000hour | 15000hour |
| Gas flow | 6L/min | 4.5L/min | 4.5L/min | 4L/min |
| Rated Voltage | 12V | 6/12/24v | 6/12/24v | 6/12/24v |
| No-load Current | 0.24A | 0.4/0.24/0.15A | ||
| Media | Most gas | |||
| Max Pressure | 120kpa | |||
| Max Vacuum | -70kpa | |||
| Ambient Temperature | 41 to 158 F(5 to 70C) | |||
| Pump size | 75.5*30.4*54.6mm | 75*31.2*57.5mm | 79*31.2*57.5mm | 79*31.2*57.5mm |
| Weight | 200g | 150g | 250g | 250g |
| Inlet&Outlet | OD 4.8mm/ID 2.6mm,hose suggestion:ID 4.0mm | |||
| Materials |
pump head Nylon, membrane EPDM , valve EPDM |
pump head Nylon, membrane EPDM / PTFE, valve EPDM / FPM |
pump head Nylon, membrane EPDM / PTFE, valve EPDM / FPM |
pump head Nylon, membrane EPDM / PTFE, valve EPDM / FPM |
| Wetted material options |
1.Optional membrane materials: 2.Optional valve materials: |
|||
Get more Technical data, Please Send message
CHINAMFG Diaphragm series gas pumps are the perfect combination of form and function. The use of a special diaphragm allows the pump to transfer both air and liquid efficiently. The compact lightweight unit offers optimum sizing for analytical equipment.
ADVANTAGES
♦ High pneumatic performance
♦ Compact size/high power density
♦ Uncontaminated flow – no contamination of the media due to oil-free operation
♦ Maintenance-free
♦ Long product life
♦ Low sound level
♦ Low power consumption
♦ Can operate in any orientation
♦ Suction
The versatility of CHINAMFG pumps allows a wide field of applications to be covered. Over many years our pumps have proved themselves in the following areas:
1.Industrial pressure and vacuum applications
2.Portable Analytical Instruments
3.Medical Equipment
4.Air Quality Sampling Monitors
5.Respiration Monitors
Performance Curve
More About Products
TOPS INDUSTRY AND TECHNOLOGY CO., LIMITED started in 2005, is the world’s leading supplier of micro
pump solutions, and won the “National High-tech Enterprise”. The company is mainly engaged in the research and development and manufacture of miniature brushless DC
pumps and miniature diaphragm pumps. 80% of the products are exported to high-end markets in Europe and
America, and are mainly used in water heaters, small household appliances, water heating mattresses, medical equipment, smart toilets, automobile circulation systems, etc. The company has always been known for its high quality and high batch consistency, and has established solid and good cooperative relations with many world-renowned brands, such as: Tesla, Whirlpool, Flextronics, Kohler, GE, Roca, KTM, Geberit, etc.
Get more Technical data, Please Send message
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Pump Head Nylon, Membrane EPDM / PTFE, Valve EPDM |
|---|---|
| Power: | Electric |
| Valve Body Type: | Pump Head Nylon, Membrane EPDM / PTFE, Valve EPDM |
| Function: | Electronic Type, Field Bus, Industrial Pressure and Vacuum Applications |
| Features: | Oil-Free,Compact Size, Corrosionresistant, Mainten |
| More Features: | High Efficiency, Can Be Mounted in Any Place |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
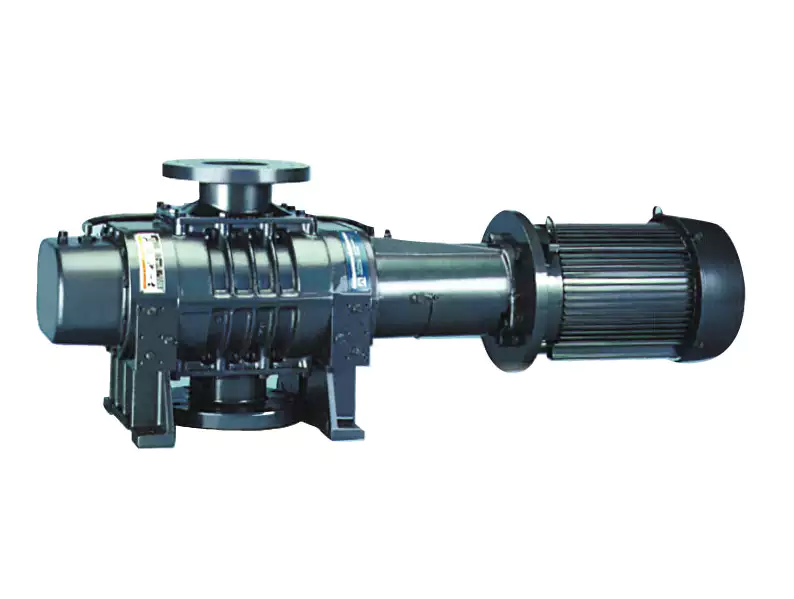

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Semiconductor manufacturing involves the production of integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices used in various electronic applications. Vacuum pumps are used extensively throughout the semiconductor manufacturing process to create and maintain the required vacuum conditions for specific manufacturing steps.
Here are some key roles of vacuum pumps in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are used in deposition processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes involve depositing thin films of materials onto semiconductor wafers to create various layers and patterns. Vacuum pumps help create a low-pressure environment necessary for precise control of the deposition process, ensuring uniform and high-quality film formation.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps are utilized in etching and cleaning processes, which involve the removal of specific layers or contaminants from semiconductor wafers. Dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching, require a vacuum environment to facilitate the ionization and removal of material. Vacuum pumps aid in creating the necessary low-pressure conditions for efficient etching and cleaning processes.
3. Ion Implantation: Ion implantation is a process used to introduce impurities into specific regions of a semiconductor wafer to modify its electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the ion implantation chamber, creating the required vacuum environment for accurate and controlled ion beam acceleration and implantation.
4. Wafer Handling and Transfer: Vacuum pumps are employed in wafer handling and transfer systems. These systems utilize vacuum suction to securely hold and manipulate semiconductor wafers during various manufacturing steps, such as loading and unloading from process chambers, robotic transfer between tools, and wafer alignment.
5. Load Lock Systems: Load lock systems are used to transfer semiconductor wafers between atmospheric conditions and the vacuum environment of process chambers. Vacuum pumps are integral components of load lock systems, creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for wafer transfer while minimizing contamination risks.
6. Metrology and Inspection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in metrology and inspection tools used for characterizing semiconductor devices. These tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) and focused ion beam (FIB) systems, often operate in a vacuum environment to enable high-resolution imaging and accurate analysis of semiconductor structures and defects.
7. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are employed in leak detection systems to identify and locate leaks in vacuum chambers, process lines, and other components. These systems rely on vacuum pumps to evacuate the system and then monitor for any pressure rise, indicating the presence of leaks.
8. Cleanroom Environment Control: Semiconductor manufacturing facilities maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication process. Vacuum pumps are used in the design and operation of the cleanroom ventilation and filtration systems, helping to maintain the required air cleanliness levels by removing particulates and maintaining controlled air pressure differentials.
Vacuum pumps used in semiconductor manufacturing processes are often specialized to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. They need to provide high vacuum levels, precise control, low contamination levels, and reliability for continuous operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are indispensable in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the creation of the necessary vacuum conditions for various processes, ensuring the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.

How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.
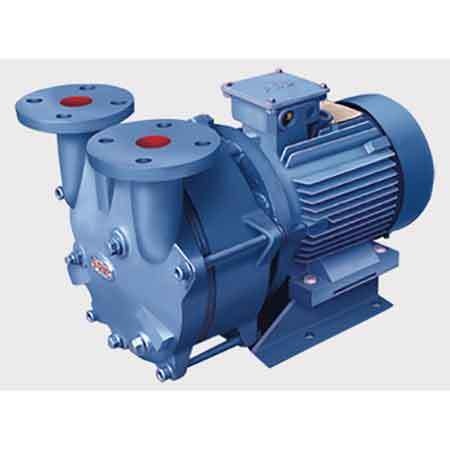

How Are Vacuum Pumps Different from Air Compressors?
Vacuum pumps and air compressors are both mechanical devices used to manipulate air and gas, but they serve opposite purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation of their differences:
1. Function:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to remove or reduce the pressure within a closed system, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. They extract air or gas from a chamber, creating suction or negative pressure.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the other hand, are used to increase the pressure of air or gas. They take in ambient air or gas and compress it, resulting in higher pressure and a compacted volume of air or gas.
2. Pressure Range:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are capable of generating pressures below atmospheric pressure or absolute zero pressure. The pressure range typically extends into the negative range, expressed in units such as torr or pascal.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the contrary, operate in the positive pressure range. They increase the pressure above atmospheric pressure, typically measured in units like pounds per square inch (psi) or bar.
3. Applications:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps have various applications where the creation of a vacuum or low-pressure environment is required. They are used in processes such as vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vacuum packaging, and vacuum filtration. They are also essential in scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, medical suction devices, and many other industries.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors find applications where compressed air or gas at high pressure is needed. They are used in pneumatic tools, manufacturing processes, air conditioning systems, power generation, and inflating tires. Compressed air is versatile and can be employed in numerous industrial and commercial applications.
4. Design and Mechanism:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to create a vacuum by removing air or gas from a closed system. They may use mechanisms such as positive displacement, entrapment, or momentum transfer to achieve the desired vacuum level. Examples of vacuum pump types include rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, and diffusion pumps.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors are engineered to compress air or gas, increasing its pressure and decreasing its volume. They use mechanisms like reciprocating pistons, rotary screws, or centrifugal force to compress the air or gas. Common types of air compressors include reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors.
5. Direction of Air/Gas Flow:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps draw air or gas into the pump and then expel it from the system, creating a vacuum within the chamber or system being evacuated.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors take in ambient air or gas and compress it, increasing its pressure and storing it in a tank or delivering it directly to the desired application.
While vacuum pumps and air compressors have different functions and operate under distinct pressure ranges, they are both vital in various industries and applications. Vacuum pumps create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment, while air compressors compress air or gas to higher pressures for different uses and processes.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16
China Hot selling GWS16 high efficiency dry type vacuum pump exhaust silencer with Good quality
Product Description
Product Description
GWT Foreline Filter
Technical Specifications
| Model | GWS16 | GWS25 | |
| Operating Pressure | Pa | 1~105 | 1~105 |
| Efficiency | % | ≥99 | ≥99 |
| Particle Size Flitered | µm | ≥2~5 | ≥2~5 |
| Filter Element | Paper, or polyester | Paper, or polyester | |
| In/Exhaust Flange | KF16 | KF25 | |
| Weight | kg | 0.25 | 0.40 |
Dimensions
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| GWS16 | φ63 | φ53 | 94 | 82 | KF 16 | 55 |
| GWT25 | φ81 | φ70 | 103 | 87 | KF 25 | 74 |
Applications
Coating, pharmaceutical, food, ceramics and hglass, vacuum furnaces, vacuum packing
Oil free Scroll Vauum Pump
Company Profile
GEOWELL VACUUM CO.,LTD. is a HI-TECH enterprise in China dedicating in manufacturing, research and development, marketing of oil free scroll vacuum pumps and vacuum compressors since 2002. GEOWELL has been providing users and partners with premium quality products that are efficient and dependable, GEOWELL believe the integration of high performance and high reliability product and service will bring the highest value to both our customers and ourselves.
FAQ
Q: How long can I get the feedback after we sent the inquiry?
A: We will reply you within 12 hours in working day.
Q: Are you direct manufacturer?
A: Yes, we are direct manufacturer with factory and international department; we manufacture and sell all our products by ourselves.
Q: When can you delivery the product to us?
A: Since we are a factory with large warehouse, we have abundant products in store, so we can delivery within 7 days after get your deposit.
Q: Can I add logo to the products?
A: Of course, but we usually have quantity requirement. You can contact with us for details.
Q: How to guarantee the quality and after sales service of your products?
A: We conduct strict detection during production from raw material come in to product delivering shipment. Every product must go through 4 steps inspection from casting, machining, assembling, and performance testing within our factory before shipment, also intact packaging test are insured.
Q: What is your warranty term?
A: There is a 12 months warranty for our export products from the date of shipment. If warranty has run out, our customer should pay for the replacement part.
Q: Is the sample available?
A: Yes, usually we send our samples by Fedex, DHL, TNT, UPS, EMS, SF, Depon, it will take around 3 to 4 days for our customer receive them, but customer will charge all cost related to the samples, such as sample cost and air freight. We will refund our customer the sample cost after receiving the order.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | exhaust silencer |
|---|---|
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
| Inlet Size: | KF16 |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What Is the Vacuum Level and How Is It Measured in Vacuum Pumps?
The vacuum level refers to the degree of pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It indicates the level of “emptiness” or the absence of gas molecules in the system. Here’s a detailed explanation of vacuum level measurement in vacuum pumps:
Vacuum level is typically measured using pressure units that represent the difference between the pressure in the vacuum system and atmospheric pressure. The most common unit of measurement for vacuum level is the Pascal (Pa), which is the SI unit. Other commonly used units include Torr, millibar (mbar), and inches of mercury (inHg).
Vacuum pumps are equipped with pressure sensors or gauges that measure the pressure within the vacuum system. These gauges are specifically designed to measure the low pressures encountered in vacuum applications. There are several types of pressure gauges used for measuring vacuum levels:
1. Pirani Gauge: Pirani gauges operate based on the thermal conductivity of gases. They consist of a heated element exposed to the vacuum environment. As gas molecules collide with the heated element, they transfer heat away, causing a change in temperature. By measuring the change in temperature, the pressure can be inferred, allowing the determination of the vacuum level.
2. Thermocouple Gauge: Thermocouple gauges utilize the thermal conductivity of gases similar to Pirani gauges. They consist of two dissimilar metal wires joined together, forming a thermocouple. As gas molecules collide with the thermocouple, they cause a temperature difference between the wires, generating a voltage. The voltage is proportional to the pressure and can be calibrated to provide a reading of the vacuum level.
3. Capacitance Manometer: Capacitance manometers measure pressure by detecting the change in capacitance between two electrodes caused by the deflection of a flexible diaphragm. As the pressure in the vacuum system changes, the diaphragm moves, altering the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
4. Ionization Gauge: Ionization gauges operate by ionizing gas molecules in the vacuum system and measuring the resulting electrical current. The ion current is proportional to the pressure, allowing the determination of the vacuum level. There are different types of ionization gauges, such as hot cathode, cold cathode, and Bayard-Alpert gauges.
5. Baratron Gauge: Baratron gauges utilize the principle of capacitance manometry but with a different design. They consist of a pressure-sensing diaphragm separated by a small gap from a reference electrode. The pressure difference between the vacuum system and the reference electrode causes the diaphragm to deflect, changing the capacitance and providing a measurement of the vacuum level.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps may have different pressure ranges and may require specific pressure gauges suitable for their operating conditions. Additionally, vacuum pumps are often equipped with multiple gauges to provide information about the pressure at different stages of the pumping process or in different parts of the system.
In summary, vacuum level refers to the pressure below atmospheric pressure in a vacuum system. It is measured using pressure gauges specifically designed for low-pressure environments. Common types of pressure gauges used in vacuum pumps include Pirani gauges, thermocouple gauges, capacitance manometers, ionization gauges, and Baratron gauges.
\
Considerations for Selecting a Vacuum Pump for Cleanroom Applications
When it comes to selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, several considerations should be taken into account. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Cleanrooms are controlled environments used in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and microelectronics. These environments require strict adherence to cleanliness and particle control standards to prevent contamination of sensitive processes or products. Selecting the right vacuum pump for cleanroom applications is crucial to maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the introduction of contaminants. Here are some key considerations:
1. Cleanliness: The cleanliness of the vacuum pump is of utmost importance in cleanroom applications. The pump should be designed and constructed to minimize the generation and release of particles, oil vapors, or other contaminants into the cleanroom environment. Oil-free or dry vacuum pumps are commonly preferred in cleanroom applications as they eliminate the risk of oil contamination. Additionally, pumps with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices are easier to clean and maintain, reducing the potential for particle buildup.
2. Outgassing: Outgassing refers to the release of gases or vapors from the surfaces of materials, including the vacuum pump itself. In cleanroom applications, it is crucial to select a vacuum pump with low outgassing characteristics to prevent the introduction of contaminants into the environment. Vacuum pumps specifically designed for cleanroom use often undergo special treatments or use materials with low outgassing properties to minimize this effect.
3. Particle Generation: Vacuum pumps can generate particles due to the friction and wear of moving parts, such as rotors or vanes. These particles can become a source of contamination in cleanrooms. When selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, it is essential to consider the pump’s particle generation level and choose pumps that have been designed and tested to minimize particle emissions. Pumps with features like self-lubricating materials or advanced sealing mechanisms can help reduce particle generation.
4. Filtration and Exhaust Systems: The filtration and exhaust systems associated with the vacuum pump are critical for maintaining cleanroom standards. The vacuum pump should be equipped with efficient filters that can capture and remove any particles or contaminants generated during operation. High-quality filters, such as HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, can effectively trap even the smallest particles. The exhaust system should be properly designed to ensure that filtered air is released outside the cleanroom or passes through additional filtration before being reintroduced into the environment.
5. Noise and Vibrations: Noise and vibrations generated by vacuum pumps can have an impact on cleanroom operations. Excessive noise can affect the working environment and compromise communication, while vibrations can potentially disrupt sensitive processes or equipment. It is advisable to choose vacuum pumps specifically designed for quiet operation and that incorporate measures to minimize vibrations. Pumps with noise-dampening features and vibration isolation systems can help maintain a quiet and stable cleanroom environment.
6. Compliance with Standards: Cleanroom applications often have specific industry standards or regulations that must be followed. When selecting a vacuum pump, it is important to ensure that it complies with relevant cleanroom standards and requirements. Considerations may include ISO cleanliness standards, cleanroom classification levels, and industry-specific guidelines for particle count, outgassing levels, or allowable noise levels. Manufacturers that provide documentation and certifications related to cleanroom suitability can help demonstrate compliance.
7. Maintenance and Serviceability: Proper maintenance and regular servicing of vacuum pumps are essential for their reliable and efficient operation. When choosing a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications, consider factors such as ease of maintenance, availability of spare parts, and access to service and support from the manufacturer. Pumps with user-friendly maintenance features, clear service instructions, and a responsive customer support network can help minimize downtime and ensure continued cleanroom performance.
In summary, selecting a vacuum pump for cleanroom applications requires careful consideration of factors such as cleanliness, outgassing characteristics, particle generation, filtration and exhaust systems, noise and vibrations, compliance with standards, and maintenance requirements. By choosing vacuum pumps designed specifically for cleanroom use and considering these key factors, cleanroom operators can maintain the required level of cleanliness and minimize the risk of contamination in their critical processes and products.

Are There Different Types of Vacuum Pumps Available?
Yes, there are various types of vacuum pumps available, each designed to suit specific applications and operating principles. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are classified based on their operating principles, mechanisms, and the type of vacuum they can generate. Some common types of vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Rotary vane pumps are positive displacement pumps that use rotating vanes to create a vacuum. The vanes slide in and out of slots in the pump rotor, trapping and compressing gas to create suction and generate a vacuum.
– Applications: Rotary vane vacuum pumps are widely used in applications requiring moderate vacuum levels, such as laboratory vacuum systems, packaging, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
2. Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm that moves up and down to create a vacuum. The diaphragm separates the vacuum chamber from the driving mechanism, preventing contamination and oil-free operation.
– Applications: Diaphragm vacuum pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical equipment, analysis instruments, and applications where oil-free or chemical-resistant vacuum is required.
3. Scroll Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Scroll pumps have two spiral-shaped scrolls—one fixed and one orbiting—which create a series of moving crescent-shaped gas pockets. As the scrolls move, gas is continuously trapped and compressed, resulting in a vacuum.
– Applications: Scroll vacuum pumps are suitable for applications requiring a clean and dry vacuum, such as analytical instruments, vacuum drying, and vacuum coating.
4. Piston Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Piston pumps use reciprocating pistons to create a vacuum by compressing gas and then releasing it through valves. They can achieve high vacuum levels but may require lubrication.
– Applications: Piston vacuum pumps are used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum furnaces, freeze drying, and semiconductor manufacturing.
5. Turbo Molecular Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Turbo pumps use high-speed rotating blades or impellers to create a molecular flow, continuously pumping gas molecules out of the system. They typically require a backing pump to operate.
– Applications: Turbo molecular pumps are used in high vacuum applications, such as semiconductor fabrication, research laboratories, and mass spectrometry.
6. Diffusion Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Diffusion pumps rely on the diffusion of gas molecules and their subsequent removal by a high-speed jet of vapor. They operate at high vacuum levels and require a backing pump.
– Applications: Diffusion pumps are commonly used in applications requiring high vacuum levels, such as vacuum metallurgy, space simulation chambers, and particle accelerators.
7. Cryogenic Vacuum Pumps:
– Description: Cryogenic pumps use extremely low temperatures to condense and capture gas molecules, creating a vacuum. They rely on cryogenic fluids, such as liquid nitrogen or helium, for operation.
– Applications: Cryogenic vacuum pumps are used in ultra-high vacuum applications, such as particle physics research, material science, and fusion reactors.
These are just a few examples of the different types of vacuum pumps available. Each type has its advantages, limitations, and suitability for specific applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors like required vacuum level, gas compatibility, reliability, cost, and the specific needs of the application.


editor by Dream 2024-05-16